|
|
The Human Organ-specific Molecule Electronic Repository (Homer) is a comprehensive database covering about 22809 proteins, 52 organs, and 4290 diseases integrated and filtered from organ-specific protein/genes and disease databases like dbEST[1], TiSGeD[2], HPA[3], CTD[4], and Disease Ontology[5]. It is the first comprehensive database that can be used to analyze, identify, and characterize organ-specific biomarkers in association with disease-organ and disease-protein relationships. The database has a web user interface that allows users to query organ-specific genes/proteins by gene, protein, organ, or disease, to browse organ-specific genes/proteins by human organ system and disease ontology, to explore a histogram of each organ-specific gene/protein, and to identify disease-related genes or disease-related organs.
The Homer is created based on four criteria: 1) organ-specific gene expression; 2) gene/protein-disease association; 3) specificity and abundance of genes/proteins across multiple target organs; and 4) disease-organ association.
As of the current release, Hommer contains 22809 proteins (IPI IDs), 5703 genes (gene IDs), 52 organs, and 4290 diseases (Mesh IDs) of which 4492 are disease-related organ-specific genes (gene IDs) and 2000 are identified as organ-specific markers (gene IDs) (Table 1). A comparison of organ-specific biomarkers in Homer against several common human tissue/organ-specific data sources is shown in Table 2.
Table 1 - Current Statistics of Database
Total Number |
Count |
Organs |
52 |
Genes |
111367 UniGene IDs |
Proteins |
76755 IPI IDs |
Organ-specific Genes |
5703 GeneIDs, 6999 UniGeneIDs |
Disease-related and Organ-specific Genes |
4492 |
Organ-specific Markers |
2000 |
Diseases |
4290 |
Table 2 - A Comparison of Human Organ-Specific Biomarkers in Hommer against Several Common Human Tissue/Organ-Specific Data Sources
|
TissueDistributionDBs[6] |
TiGER[7] |
TiSGeD[2] |
HPA[3] |
Homer |
Organ coverage |
40 |
30 |
18 |
24 |
52 |
Gene coverage |
1359* |
4283** |
957*** |
74 |
5706 |
Last Updated |
2010 |
March 2008 |
July 2010 |
Jan 2011 |
April 2011 |
Criteria for organ-specific genes |
TissueSpecificityIndex |
p-value<1e-3.5
EE>5 |
SPM |
Exclusively detected in a single cell |
p-value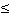 1e-5 1e-5
RZ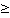 4 4
AE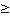 10 10
RE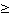 4 4 |
Expression Value |
Relative expression |
Yes |
No |
No |
Relative Expression |
Plasma Detectability |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Disease Association |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
*1359 gene IDs was filtered out from 54, 576 human unigene IDs with TissueSpecificityIndex = 1. We used TissueSpecificityIndex = 1 as the website doesn¡¯t recommend any criteria for us to derive organ-specific genes.
** 1494 of 6698 Unigene IDs were retired.
*** 957 gene IDs was filtered out from 2423 gene IDs with SPM 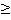 0.9. We used SPM 0.9. We used SPM 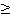 0.9 as the website doesn¡¯t recommend any criteria for us to derive organ-specific genes. 0.9 as the website doesn¡¯t recommend any criteria for us to derive organ-specific genes.
1.Boguski MS, Tolstoshev CM, Bassett DE, Jr.: Gene discovery in dbEST. Science 1994, 265(5181):1993-1994.
2.Xiao SJ, Zhang C, Zou Q, Ji ZL: TiSGeD: a database for tissue-specific genes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26(9):1273-1275.
3.Uhlen M, Oksvold P, Fagerberg L, Lundberg E, Jonasson K, Forsberg M, Zwahlen M, Kampf C, Wester K, Hober S et al: Towards a knowledge-based Human Protein Atlas. Nat Biotechnol 2010, 28(12):1248-1250.
4.Davis AP, King BL, Mockus S, Murphy CG, Saraceni-Richards C, Rosenstein M, Wiegers T, Mattingly CJ: The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: update 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39(Database issue):D1067-1072.
5.Osborne JD, Flatow J, Holko M, Lin SM, Kibbe WA, Zhu LJ, Danila MI, Feng G, Chisholm RL: Annotating the human genome with Disease Ontology. BMC Genomics 2009, 10 Suppl 1:S6.
6.Kogenaru S, del Val C, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Glatting K-H: TissueDistributionDBs: a repository of organism-specific tissue-distribution profiles. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts: Theory, Computation, and Modeling (Theoretica Chimica Acta) 2010, 125(3):651-658.
7.Liu X, Yu X, Zack DJ, Zhu H, Qian J: TiGER: a database for tissue-specific gene expression and regulation. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9:271.
|
|
 Homer
Homer